If you’re looking for ways to reduce your household expenses, switching to solar energy might just be what you need. It’s a clean and renewable power source that can help you save money on your monthly electricity bills.
Although the upfront cost of installing solar panels can be a major deterrent for your finances, you have two options when switching to solar: leasing and buying.
Leasing solar panels means renting them from a solar provider who will handle the installation, maintenance, and repair costs. On the other hand, buying solar panels means owning them outright and being responsible for all associated costs.
To help you decide which option suits you, check the infographic below about leasing vs. buying solar panels’ pros and cons.
Pros and Cons of Leasing Solar Panels
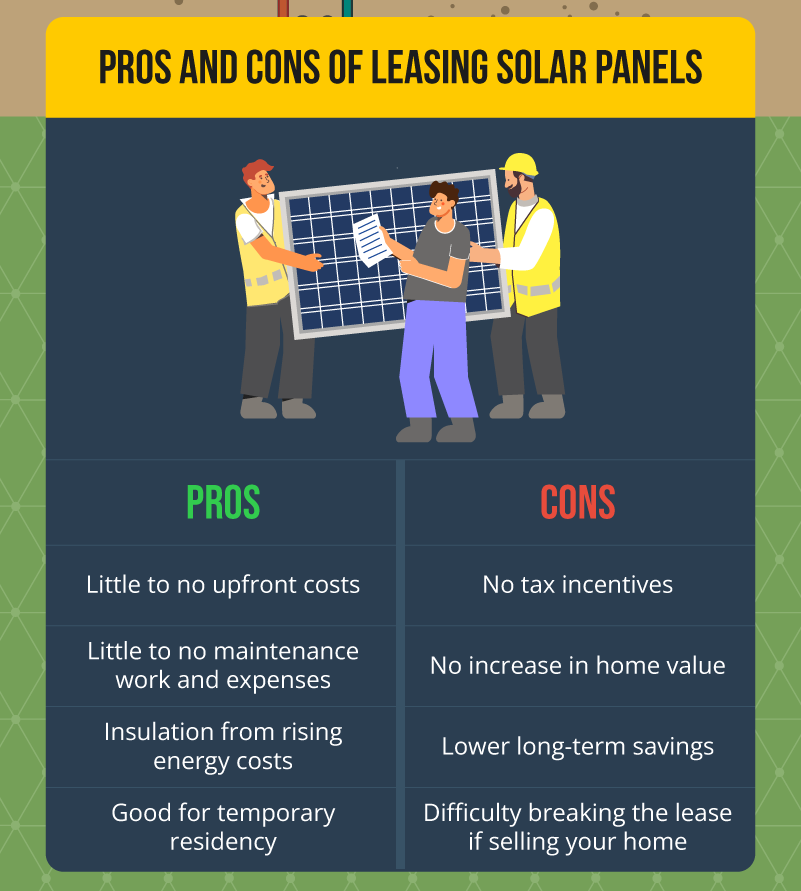
Leasing solar panels is ideal if you want to switch to solar power but don’t have the upfront capital for the system. However, it comes with potential drawbacks. Consider the pros and cons of leasing solar panels.
Pros
- Little to no upfront costs
Leasing allows you to switch to solar energy with little to no out-of-pocket expenses. This benefit makes solar energy accessible even if you don’t have the upfront capital to buy a solar energy system outright, helping you save costs while reducing your carbon footprint.
- Little to no maintenance work and expenses
Solar panel providers are responsible for maintenance and repair, letting you save time, money, and effort. In this setup, you are not accountable for any damage the solar system might have during the lease period. Moreover, leasing companies provide warranties for their equipment as part of maintenance.
- Insulation from rising energy costs
Solar panels save you from buying energy from the national power grid. Leasing them entails paying a fixed monthly fee to avoid the impact of rising energy costs, helping control your energy expenses.
- Good option for temporary residency
Leasing can be a cost-effective way to take advantage of solar energy without making a long-term commitment. As such, it’s ideal if you’re currently renting a home. If you move out before the end of the lease term, you can typically transfer the lease to the new tenant or end the lease early.
Cons
- No tax incentives
Under the Renewable Energy Act of 2008, solar panel users can receive fiscal and non-fiscal incentives. However, you can’t take advantage of these benefits since you don’t own the solar panels. While only a bonus to using solar energy, these incentives can offer money savings in the long run.
- No increase in home value
Leasing solar panels means you can’t make them a distinct feature of your home, making it less attractive to buyers if you sell your property. Budget-conscious home buyers prefer purchasing a home already equipped with solar energy instead of continuing the monthly payments for a leased system.
- Lower long-term savings
Although leasing may have little to no upfront costs and can provide immediate access to solar energy, the monthly lease payments will continue throughout the lease term. If you repeatedly renew your lease for years, the cumulative total of your monthly payments may end up bigger than the cost of buying new solar panels. As a result, you’ll pay significantly more for the leased solar panel system over time.
- Difficulty breaking the lease if selling your home
One of the potential downsides of leasing solar panels is that it can be challenging to break the lease if you decide to sell your home. Most leases require that the new homeowner takes over the lease, which might not be part of potential buyers’ plans. Here, finding a buyer willing to take on the remaining lease payments may be difficult if the lease has a few months or years left.
Pros and Cons of Buying Solar Panels
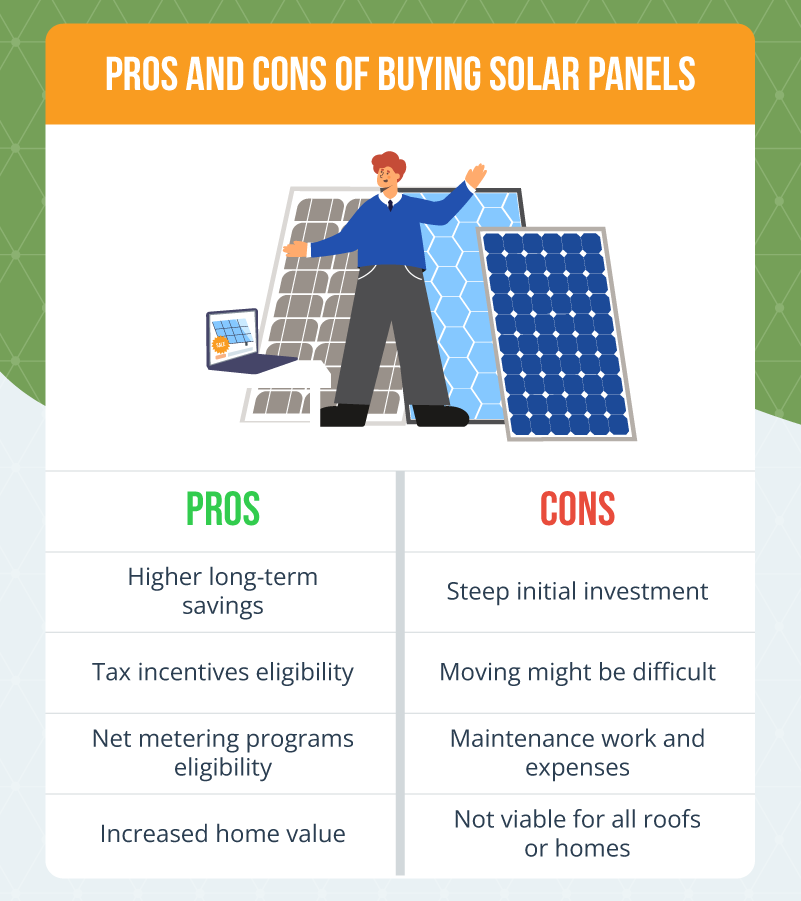
If you have enough capital to buy solar panels, it may be the more cost-effective option in the long run. However, there are still some challenges to consider. Below are the pros and cons of buying solar panels for your household.
Pros
- Higher long-term savings
Solar panels for your home allow you to reduce your energy consumption from using home appliances. As a result, you can save money in managing several aspects of your household in the long run.
For instance, solar energy can be particularly beneficial for powering high-energy appliances such as air conditioners, which can significantly increase monthly electricity bills. This is especially true during summer when rising temperatures compel you to use air conditioners for long periods.
- Tax incentives eligibility
Installing solar systems may make you eligible for tax incentives like the Investment Priorities Plan, which provides tax exemptions and other benefits for investing in renewable energy. Through this incentive, you can reduce the overall cost of your solar system and potentially recoup your initial investment faster.
- Net metering programs eligibility
You can also qualify for net metering if you invest in solar panels for the long term. In particular, you may sell excess energy to the grid and receive credit on your utility bills. Through this billing method, you can take advantage of more energy during the day, export surplus power to the grid, and reduce your electricity bills in the future.
- Increased home value
Nowadays, solar panels serve as a valuable home upgrade and a sustainable energy solution, increasing the value of residential properties equipped with them.
Installed solar systems may appeal to certain buyers looking to save money on energy bills and reduce energy consumption. If your home is in a remote or rural area, solar energy systems can help you better attract homebuyers. Think remote workers who want to escape congested cities.
Cons
- Steep initial investment
Buying solar panels requires a steep initial investment, whether in cash or through an installment plan. It’s not ideal if you’re not financially capable of covering installation and maintenance costs.
- Moving might be difficult
Buying solar panels may not be practical if you don’t have a permanent home. For instance, removing and re-installing the panels as you move homes might be challenging. On the other hand, you might have difficulty selling your home if you promote it to another homeowner who doesn’t see value in solar energy.
- Maintenance work and expenses
If you own solar panels, you’re responsible for the upkeep and repair of the system. Whether you care for it or hire professionals to handle the work, you must exert effort or spend more on maintenance. Luckily, solar panels generally have low maintenance needs. You can clean them with running water and soap, then wipe them with a clean cloth.
- Not viable for all roofs or homes
Due to several factors, buying solar panels may not be a viable option for all roofs or homes. Firstly, your roof should have enough space to accommodate the solar panels and maximize exposure to sunlight. If the roof is shaded or has an irregular shape, the panels might not be as efficient.
Additionally, your roof’s structural integrity should be strong enough to support the weight of the heavy solar panels. Lastly, your home should be situated in an area with enough sunlight throughout the year to make solar energy production worthwhile.
Leasing vs. Buying Solar Panels: Key Differences
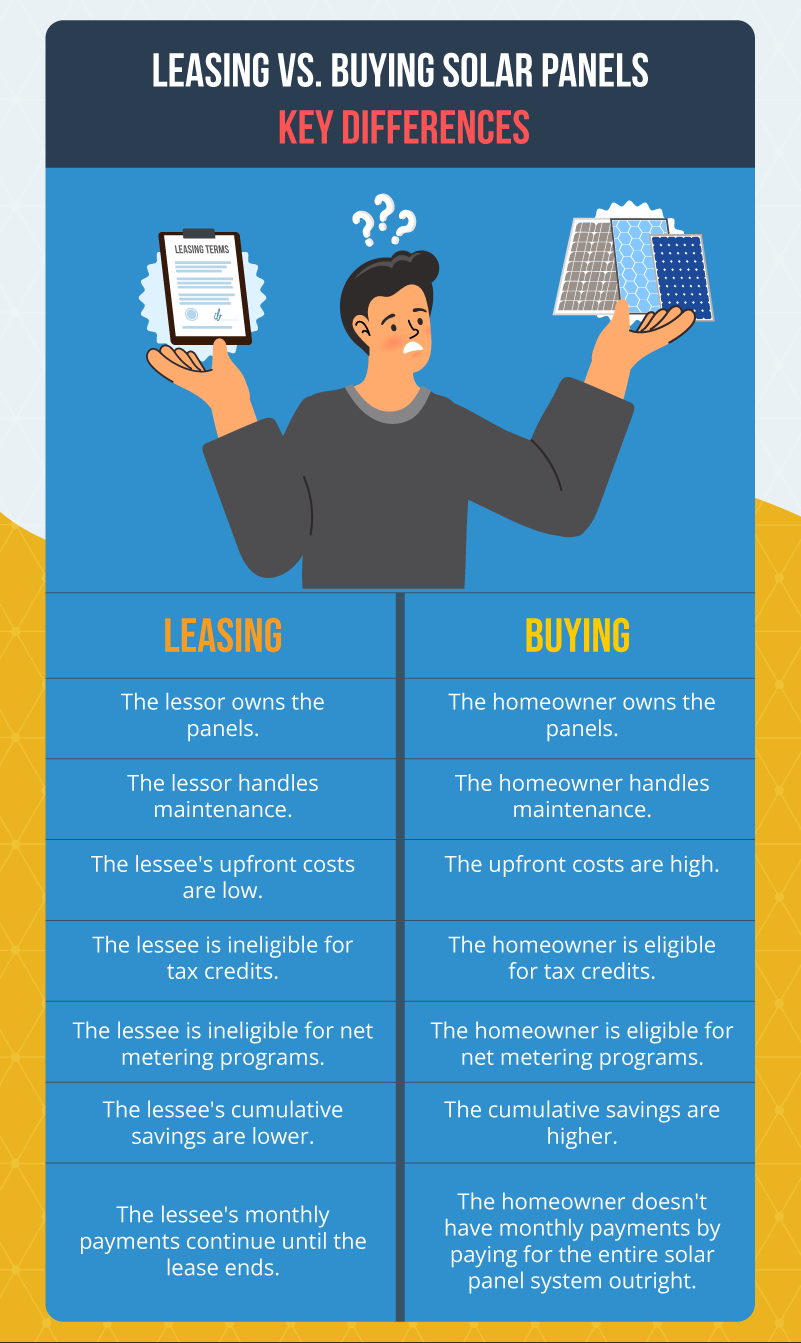
If you’re still unsure if you’d rather buy or lease solar panels, here are the key differences between the two to help you finalize your decision.
Leasing Solar Panels
Leasing is an economical way to switch to solar energy, which is why many homeowners consider it. However, leasing comes with conditions that you should know beforehand.
- The lessor owns the panels.
- The lessor handles maintenance.
- Your upfront costs are low.
- You may be ineligible for tax credits or net metering programs.
- Your cumulative savings are lower.
- Your monthly payments continue until the lease ends.
These conditions mean you save on upfront costs through leasing since you don’t have to buy solar panels and spend on their maintenance. However, your lifetime savings are considerably lower than if you purchase solar panels. This is because owning solar panels makes you eligible for tax credits and net metering programs.
In simpler terms, leasing is ideal if you can’t afford the initial investment. If you are renting or plan to move soon, a short-term lease allows you to change residences without worrying about transporting the panels.
Buying Solar Panels
Buying solar panels is a significant investment. But how do you know if you’re ready to take this step? First, consider these conditions that come with buying solar panels.
- You own and maintain the panels.
- The upfront costs are high.
- You are eligible for tax credits and net metering programs.
- The cumulative savings are higher.
- You don’t have monthly payments since you pay for the entire solar panel system outright.
Summing up, owning solar panels may qualify you for tax incentives and net metering programs. Combining these two benefits with the cost savings of switching to solar energy, buying solar panels gives you higher lifetime savings than leasing. Plus, solar panels increase your property’s value and give you an advantage if you sell the house.
Ultimately, buying solar panels is the best option for maximizing your return on investment.
Switch to Solar Now
Choosing between leasing and buying solar panels depends on your needs, budget, home ownership status, and energy needs. Leasing is cost-effective but offers no ownership and lower long-term savings. On the other hand, buying has bigger upfront costs but higher savings and home value potential. With the points above, you can better understand the pros and cons of buying versus leasing solar panels.
Then, look for a solar panel provider to assist you from inquiry to installation and maintenance. SolarNRG offers various residential solar solutions to help you reduce your carbon footprint while enjoying affordable, reliable, and uninterrupted power.
Contact us today to learn more about solar solutions.


Recent Comments