It’s common to think of solar power as the only alternative to traditional energy due to its massive advertising exposure. Solar has a tremendous demand worldwide, with roughly two-thirds (68%) of the population favoring this power source.
However, the fact of the matter is there are several types of solar energy. As more people develop an interest in eco-friendly energy solutions that continue to unfold, it’s imperative to understand the various facets of solar technology.
In line with that goal, this infographic guides you through the different types of solar energy to help build a more sustainable future.
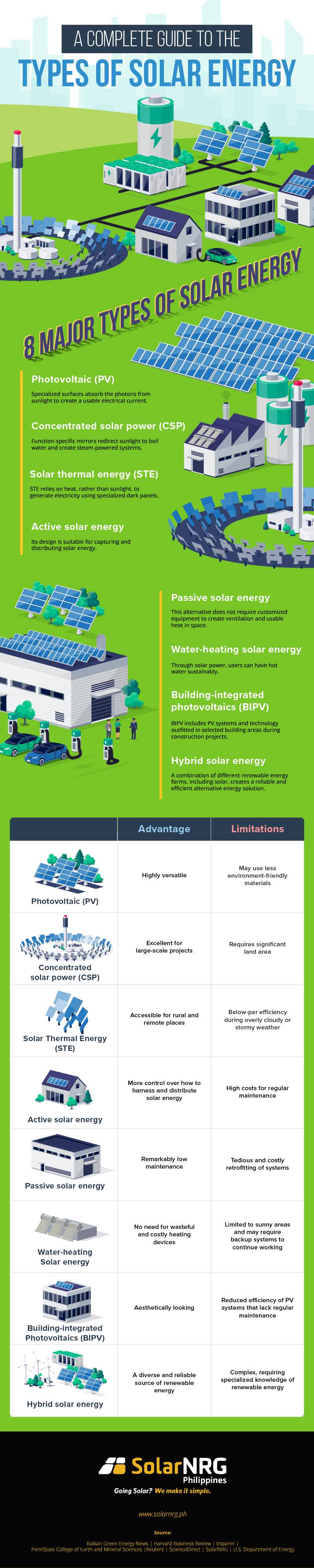
8 Major Types of Solar Energy
Solar energy provides numerous benefits to businesses. You only need to learn how to harness or use the different types of solar energy. Then, you can choose the right solar panel installer for your needs.
1. Photovoltaic (PV)
In simple terms, photovoltaic (PV) energy involves using solar cells to convert sunlight into electricity directly. PV systems rely on the photoelectric effect, which occurs when light, specifically photons, strikes a surface of specialized material. Electrons then shoot outward from the surface, creating a usable electrical current.
As mentioned, specialized surfaces make up the solar cells. Typically, the larger the surface, the more sunlight you can capture. It’s why you’ll often see large solar panels on rooftops and large open spaces.
Advantages:
PV systems are among the most popular worldwide, making them a highly accessible solar energy technology. Apart from their availability, they’re versatile, allowing you to install them on different surfaces and scales.
Limitations:
The downside is that PVs can also pose an environmental challenge in the materials it uses. According to the Harvard Business Review, some governments deem PV solar panels as hazardous waste because of the chemicals and materials that go into producing these technologies. Ideally, you partner with a responsible producer to ensure your PV solar system does little to no environmental harm.
2. Concentrated solar power (CSP)
As the name suggests, concentrated solar power (CSP) involves focusing sunlight into a narrow area to produce heat. These types of systems use large mirrors—known as heliostats—to direct sunlight toward a receiver or power tower filled with a heat-transfer fluid, creating steam. CSP works similarly to a steam engine, powering turbines for electricity generation.
These are common makeups and images to visualize what a standard solar farm looks like.
Given the size of the system, CSPs are more common for large-scale industrial projects. For instance, Dubai opened the world’s largest concentrated solar power plant at the tail end of 2023.
Advantages:
CSP systems are a staple type of solar energy system for generating renewable energy on a large scale. Not only can it capture a great deal of solar energy, but it can also store and distribute it reliably. The central power tower can hold the system’s steam and continue generating electricity overnight.
Limitations:
The primary drawback of CSP systems is that they typically require a vast land area to operate effectively. These have financial and environmental costs. Plus, constructing CSP systems may disturb ecosystems and wildlife.
3. Solar thermal energy (STE)
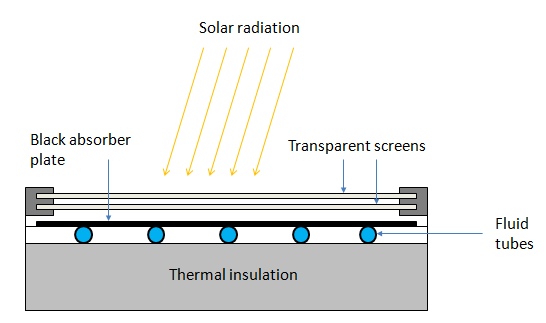
Instead of using the sun’s light, solar thermal energy (STE) relies on its heat for diverse applications. STE is what makes CSP and water-heating solar energy possible. Different solar thermal energy collectors suit certain applications better than others. For instance,
flat-plate collectors rely on the property of dark surfaces to absorb heat more effectively. Fluid tubes then receive heat collected from the black absorber plate and transfer it into usable energy.
For a better understanding of the process, here’s a visual guide:
Advantages:
Solar thermal energy is excellent for rural and remote places that receive a lot of sunlight. Installed STE systems also have relatively low operating costs.
Limitations:
They require large land areas with regular sunlight, as cloudy and stormy weather can severely impede the system’s efficiency.
4. Active solar energy
Active solar energy systems use mechanical and electrical components to collect and store solar energy efficiently. Solar panels are active solar energy systems since they sit on roofs or large plots of land to gather the sun’s energy.
Advantages:
Active solar energy systems give you more control over how you want to harness and use the solar power it generates. You can easily adjust these systems based on factors such as weather conditions or your current power consumption. Since you’re in direct control of it, it’s much easier to calculate your solar panel costs and return on investment.
Limitations:
It’s worth noting that these types of solar energy systems tend to be pricey. Some are also more complex than a passive system, with various wiring, pumps, and controls to manage. This setup type also requires more regular maintenance and upkeep, which can add to the lifetime cost of your investment.
5. Passive solar energy
Unlike other types of solar energy, passive solar power doesn’t require specialized devices to create ventilation and usable heat in spaces. For example, large windows that allow a significant amount of sunlight into the building.
Architects typically consider passive solar energy systems in the building design to reduce the need for mechanical devices when harnessing the sun’s energy.
Advantages:
What makes passive solar energy so advantageous is how low maintenance it is. There are minimal operating costs because it’s part of the building’s architecture. It’s a sustainable way to enjoy the benefits of sunlight without needing complicated technologies.
Limitations:
Efforts to establish a passive system can be tedious. It depends on how successfully you go through the building’s design phase. Methods like retrofitting passive solar energy features, such as a south-facing window, may allow you to make significant renovations and reconstructions.
6. Water-heating solar energy
Solar water heaters have a simple operation. First, flat-plate collectors absorb sunlight. Then, the heat the device collects transfers to a tank of stored water, increasing its temperature. The newly heated water then flows out of the tank and into your space or property.
Water-heating solar energy is common for providing warmth in large residential and commercial spaces, reducing dependence on other heating methods that could produce environmental waste.
Advantages:
Solar water heaters allow homeowners and commercial property owners to harness the sun’s energy to enjoy warm water sustainably. They’re also a sustainable way to lower your electric bill. These types of solar energy systems benefit regions with considerable sunlight.
Limitations:
Areas that don’t receive much sunlight may not be able to enjoy these types of systems as much. Also, they may require backup water heating systems and tech, which involves additional cost and space to install.
7. Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV)
Architects and engineers can integrate photovoltaics in many areas of the building under construction, such as the façade. They do so by replacing glass windows with semi-transparent, thin-film solar panels. These types of PVs generate electricity while adding to the building’s aesthetics.
Advantages:
The most significant benefit of BIPV is that it’s integrated into a building’s design. There’s no need for property or building owners like yourself to look for additional space for PV solar panels. It also lends a consistent aesthetic design to the whole building.
Limitations:
Like the other solar energy types discussed here, there are a few caveats to BPIVs that you must consider before investing in them. The system’s efficiency may become an issue. For instance, constructing windows with PVs, instead of installing a dedicated panel on the roof, can limit how much of the sun’s energy it can capture.
Additionally, there is also the challenge of regular maintenance. Without it, BIPVs can quickly become an aesthetic nuisance that serves no purpose.
8. Hybrid solar energy
Hybrid solar energy combines different renewable energy technologies, from those that harness the sun to the wind, to generate electricity consistently. Leveraging the strengths of the different types of solar energy increases hybrid solar energy’s overall reliability. The hybrid type of solar energy has a ready market. In Cebu, a ₱60 million solar farm investment now energizes the country’s longest bridge.
Advantages:
The benefits of hybrid solar energy systems are encompassing, from optimum solar energy production to complete reliability.
Limitations:
Then again, harnessing hybrid solar energy is a challenging task. It requires specialized knowledge for installation and maintenance, which can increase the overall management costs. The initial investment could also be higher than that of other standalone systems, posing a barrier to renewable energy advocates.
Understanding Everything Under the Sun
Although the sun will remain the same for years to come, harnessing its power continues to evolve. Different types of solar energy systems and technologies allow more and more people to invest in alternative power sources while helping save the environment.
There is no one best type of solar energy. Ultimately, your choice must depend on your goals and current property situation— whether you’re investing in solar panels to energize a building in the city or a home in the province. Regardless of what you choose, once you do, it’s best to work with an experienced brand to help you achieve your solar power goals.
SolarNRG has over 20 years of international solar experience. You can rely on our solutions to harness solar energy for industrial or commercial use. Contact us now to learn more about what we can do for you.

Recent Comments