Individual solar panels aren’t enough. According to the International Energy Agency, the world must generate 25% more solar energy yearly until 2030 to reduce all carbon emissions by 2050.
With 3.6% of the world’s electricity coming from solar energy, it’s one of the most popular renewable sources. Fortunately, different countries are already taking action to generate more solar energy. The Philippines, for instance, generates almost half (47%) of its energy from renewable sources.
In recent years, the world has been facing a renewable energy crisis. Using fossil fuels has led to a rise in global warming, climate change, and a depletion of our natural resources. That is why corporations and governments are turning to solar farms as solutions.
With how important solar farms are to humanity’s future, it helps to learn more about them and how they work. Read the infographic below to discover the science behind solar farms.

What are Solar Farms?
Solar farms, also called solar power stations or solar parks, are massive collections of photovoltaic (PV) solar panels. You may think of it as larger-scale solar-powered microgrids. They operate similarly to fossil fuel power plants, which generate enormous energy for businesses and communities—except they’re far more sustainable and environmentally friendly.
Electricity produced by solar farms ranges from 1 megawatt (MW) to 800 MW. Take India’s Bhadla Solar Park, for instance. It’s 5,700 hectares and generates enough power for 4.5 million homes—2,250 MW or 2.25 gigawatts (GW)—making it the largest solar farm on the planet.
Solar farm owners may need a power purchase agreement before building their solar farms.
5 Types of Solar Farms
According to typical solar farm installation metrics, companies will need at least one hectare per one-megawatt installation. There are generally five types of solar farms, each occupying space differently and serving unique purposes.
Of course, no type is better than the other; it depends on the owner’s purpose for building their solar farms.
1. Ground-mounted solar farms
Ground-mounted solar farms are a popular option for people who want to slowly build their solar farms or begin using solar panels at home. They’re installed directly on the land, typically in large fields or yards. The caveat of ground-mounted solar farms is that they tend to be costly because of the labor costs of preparing the land area for the panels.
2. Rooftop solar farms
If owners have no land space for ground-mounted solar farms, rooftop solar farms can be a similarly viable solution to their renewable energy concerns. They’re more cost-effective than building an entirely new structure just for solar power generation, and they don’t require clearing land or digging holes.
3. Floating solar farms
Floating solar farms are a new and innovative way to provide electricity to people. Without being on land, they can be positioned over the surface of a lake, industrial pond, or reservoir.
Floating solar farms are an ideal solution for corporations that can’t afford to lose land space. They can generate more electricity when combined with ground-mounted solar farms. One of the largest floating solar farms in the world is the 1.2-GW Saemangeum Floating Solar Power Project off the coast of South Korea.
4. Utility-scale solar farms
Utility-scale solar farms are ideal for industrial solutions because these owners sell their electricity to wholesale buyers rather than individual consumers.
Most utility-scale solar farms use concentrating solar-thermal power (CSP) technology, which uses mirrors to reflect sunlight into heat-transferring liquid. The liquid boils, creating steam, which spins a turbine and generates electricity.
Plenty of utility-scale solar farms also provide solar energy storage services, allowing them to provide electricity during the evening.
5. Community solar farms
Community solar farms are shared spaces. They allow members of a community or municipality who might not have room for their own solar panels to access renewable energy by subscribing to the services of a solar farm.
Although many different types of solar farms exist, they all fundamentally work the same.
How Do Solar Farms Work?
How do solar farms generate electricity? Sunlight is converted into electricity by solar farms’ solar panels, which people may then use to run their homes, places of business, and machinery. Knowing how the process works will help you decide whether or not investing in a solar farm makes sense for you if you’re thinking about doing so.
1. Photovoltaic cells (PV) absorb sunlight
Solar farms are powered by tiny photovoltaic cells or solar cells. These cells are typically made of silicon and absorb photons from sunlight to transform them into usable electricity in a process called the photovoltaic effect, discovered by Edmond Becquerel in 1839.
PV cells are made of two semiconductors stacked on top of each other. One side has a negative charge because it has many electrons; the other is positive and lacks electrons. The photons from the sun’s light knock electrons loose from the top layer, attracting them to the semiconductor below.
When electrons move, they create a current that semiconductors push out of the PV cell. An electrical load captures the energy of this current. Electrons exit the semiconductor layer, pass through the electric load, and then return to the PV cell to restart the cycle.
2. Solar panels spread energy
The solar panel, housed in a metal frame that covers the solar cells in glass, provides space for the numerous connected PV cells to direct their electrical current through wires. The electrons’ energy is direct current (DC) electricity, which then surges toward the panel’s wiring, flowing toward inverter and transformer systems.
3. Inverters and transformers convert electricity
Solar energy from the PV cells flows toward inverters and transformers, which receive DC and output AC. After, a transformer moderates and adjusts the voltage of the outgoing AC.
4. Inverters and transformers transfer the energy to the grid
After the inverters convert the electrical current from DC to AC and transformers adjust the voltage, the electricity is ready for regular consumption. Solar farms have high-voltage power lines that transmit the electricity to the grid, making it available to the public.
Solar farms use a process that’s straightforward, scientific, and effective. As you may have noticed, the process of solar farms is complex. It involves many parts—parts you’ll need to familiarize yourself with to understand how solar farms work and to help you diagnose solar panel problems.
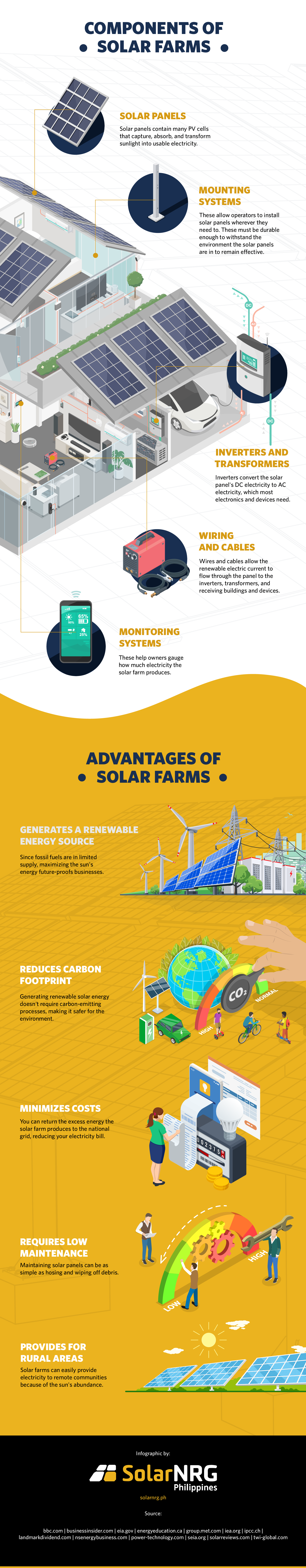
Components of Solar Farms
Solar farms have multiple components that produce clean, renewable energy. You may work with solar panel installation experts to customize your farm to your unique needs, but here are some basic parts you should include in every installation.
1. Solar panels
Solar panels contain many PV cells that capture, absorb, and transform sunlight into usable electricity. While solar panels for homes typically come in a monocrystalline or polycrystalline material, most business establishments use thin-film solar cells (TFSCs). These TFSCs are lightweight, flexible, and aesthetically pleasing, ideal for different applications a business needs.
2. Mounting systems
The mounting system is one of the most important factors when buying solar panels. It must be durable enough to withstand the solar farms’ environment, such as during a typhoon.
There are two main types of mounting systems: fixed and tracking. As the name implies, fixed mounting systems are stationary and can’t be moved by the user. The placement and direction of the solar panel are important considerations since you can’t move it easily after installation.
Tracking mounting systems allow you to adjust your solar panels horizontally and vertically to aim them at the sun. They’re a more effective way to get energy but also more expensive.
3. Inverters and transformers
The inverter and transformer are two components that are vital to the distribution of electricity from panels to people. The inverter converts the incoming DC electricity, which most consumer electronics require, into 240 volts of AC. The transformer gives operators control of how much voltage the outputting ACs are.
4. Wiring and cables
Solar wires, either single or stranded, allow renewable energy to travel around the solar panel system. They’re from the PV cells to the inverters and transformers. Some solar farms use copper and aluminum wiring.
Copper wire has excellent conductivity, allowing it to carry more electrical current than aluminum. However, aluminum wires are often more affordable and rigid than copper wires.
On the other hand, solar cables are built to be much more durable and withstand different weather conditions and high temperatures. Solar farm owners primarily use these to connect solar panels to power grids.
5. Monitoring systems
Monitoring systems like solar power meters are crucial, allowing you to see how much energy your farm produces. They’re great with a solar power calculator to help you determine how much energy the farm has.
Monitoring systems also allow you to gauge your solar panel efficiency and identify problems with the system, such as if it produces significantly less electricity than usual.
You’ll need to monitor how much solar energy the solar farms produce to take advantage of net metering, where you can sell the excess solar power back to the grid and reduce your next electricity bill.
These solar farm components work together to provide owners with multiple advantages.
Advantages of Solar Farms
Solar farms are a significant investment. Suppose you’d have to spend PHP25,000 for a single panel, but the solar farm you want to create requires roughly 100 panels. The farm’s total cost would be PHP 2,500,000—a significant price you wouldn’t want to spend too quickly.
Before you agree to pay such a large sum, you need to get a clear sense of the advantages of going solar and how you might be able to calculate its return on investment (ROI).
1. Generates a renewable energy source
The Earth’s fossil fuels have taken centuries to form. Once they run out, people will need to find other energy sources. Solar energy is the most abundant energy available, 10,000 times more than people need. It’s a great way to future-proof your business.
2. Reduces carbon footprint
The only way to use non-renewable energy sources like oil and gas is to burn them. Burning them emits greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, which could harm the environment and accelerate climate change.
A renewable energy source that doesn’t release greenhouse gases is solar energy. Unlike fossil fuels, solar farms don’t require a burning process to produce electricity. It’s one of the biggest environmental benefits, and why it’s also known as clean energy.
3. Minimizes costs
The sun is the most abundant source of energy on the planet. Harnessing its power with solar farms will allow people to save on their electricity bills.
The government is pushing to make establishments more sustainable, so many offer solar incentives to those who’ve switched to solar power. These benefits include cash incentives and tax credits. The cost-effectiveness of a solar panel system makes it a viable investment for many industries, from car manufacturing plants to agricultural farms.
4. Requires low maintenance
Although maintaining solar panels is a simple process, there’s a lot of labor involved in keeping solar panels functional. Hosing out debris, cleaning them with soap, and wiping them dry with a clean cloth are usually enough to keep the solar panels in good shape.
However, since solar farms have hundreds of solar panels, hiring professionals to maintain them properly benefits you.
5. Provides for rural areas
In some countries, like the Philippines, rural areas affected by typhoons can’t receive enough electricity to keep their lives running smoothly. Of the many advantages of solar farms, one of the most important is that they only require sunlight to remain operational and provide electricity to whoever needs it.
Reap the Benefits of Solar Farms
Solar farms will be crucial as the Philippines and the world rely more heavily on renewable energy. They’re cost-effective solutions that provide much-needed clean energy to communities and corporations.
If you’re looking to invest in solar farms, it’s important to understand how they work. To get started, you can work with solar energy experts to help you decide where and how to install your solar farms best.
SolarNRG has more than two decades of solar panel installation experience for residential, commercial, and industrial clients. Contact us today to learn how we can help you begin harnessing the sun’s energy to energize your business.

Recent Comments